18. Undistort and Transform
Undistort and Transform Perspective
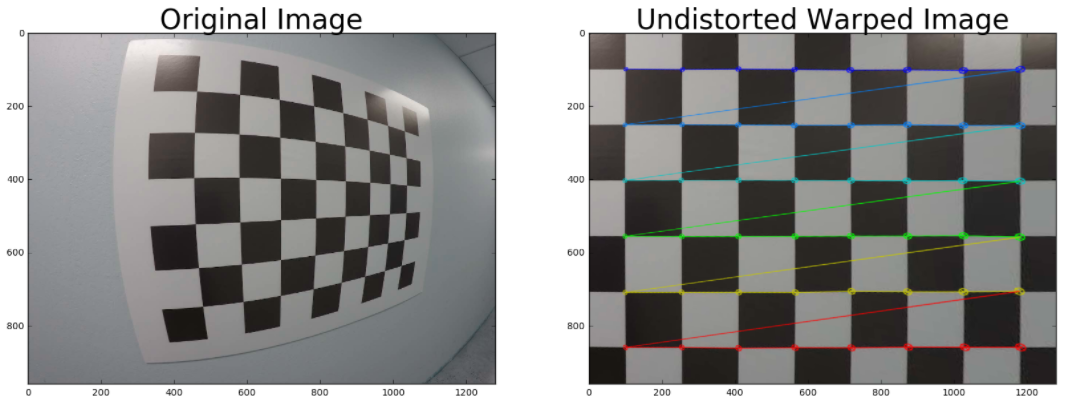
Here's a tricky quiz for you! You have now seen how to find corners, calibrate your camera, undistort an image, and apply a perspective transform. Now it's your chance to perform all these steps on an image. In the last quiz you calibrated the camera, so here I'm giving you the camera matrix,
mtx
, and the distortion coefficients
dist
to start with.
Your goal is to generate output like the image shown above. To do that, you need to write a function that takes your distorted image as input and completes the following steps:
-
Undistort the image using
cv2.undistort()withmtxanddist - Convert to grayscale
- Find the chessboard corners
- Draw corners
- Define 4 source points (the outer 4 corners detected in the chessboard pattern)
- Define 4 destination points (must be listed in the same order as src points!)
-
Use
cv2.getPerspectiveTransform()to getM, the transform matrix -
use
cv2.warpPerspective()to applyMand warp your image to a top-down view
HINT:
Source points are the x and y pixel values of any four corners on your chessboard, you can extract these from the
corners
array output from
cv2.findChessboardCorners()
. Your destination points are the x and y pixel values of where you want those four corners to be mapped to in the output image.
If you run into any errors as you run your code, please refer to the Examples of Useful Code section in the previous video and make sure that your code syntax matches up! For this example, please also refer back to the examples in the Calibrating Your Camera video. You can also download the distortion pickle file and test image used in the below quiz if you'd like to run the below code on your own machine.
Start Quiz: